
Google is a multinational technology company specializing in internet services and products. It is a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. and is one of the most influential and valuable companies in the world. Founded in 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, Google has transformed from a simple search engine into a diversified tech giant with products and services across various sectors, including online advertising, cloud computing, software, hardware, and artificial intelligence.

History
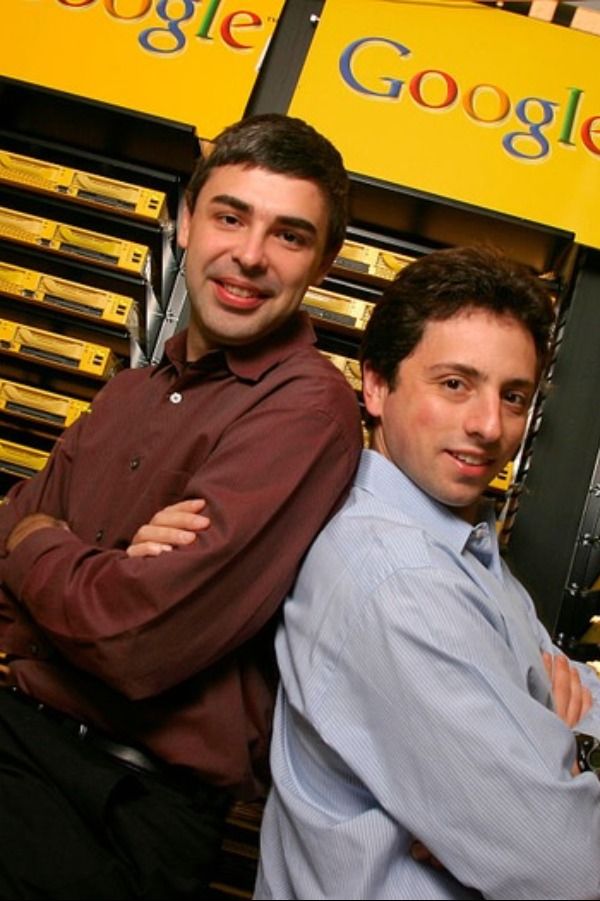
Google's inception dates back to 1996 when Larry Page and Sergey Brin, two PhD students at Stanford University, collaborated on a research project. They aimed to develop a search engine that would organize the vast and growing information on the internet in a more relevant manner.
This project evolved into a search engine initially called "BackRub", based on a unique algorithm that ranked web pages by analyzing their backlinks (links from other sites). This was a significant breakthrough, as existing search engines at the time relied on simple keyword matching, while BackRub’s PageRank algorithm considered the number and quality of links pointing to a page, offering more accurate and relevant results.
In 1998, the duo registered the domain Google.com, a name derived from "googol," symbolizing their mission to organize a seemingly infinite amount of information. Google’s minimalist design, fast speed, and relevant results quickly attracted users, and the company began to grow. In 1999, they received $25 million in venture capital funding from Sequoia Capital and Kleiner Perkins, which helped accelerate their growth. By the early 2000s, Google was the leading search engine, surpassing rivals like Yahoo and AltaVista.
Google's initial focus was purely on search, but it soon diversified into various other internet services. The company’s Initial Public Offering (IPO) in 2004 was a major milestone, valuing it at $23 billion. It signaled Google’s growing importance in the tech world, and this infusion of capital allowed it to invest in products like Gmail, Google Maps, and Android. Google’s acquisition of YouTube in 2006 for $1.65 billion further expanded its influence, making it a dominant player in the world of online video.

Google Search
Google Search is the foundation upon which the entire company was built. Launched in 1998, the search engine quickly became the most popular in the world due to its innovative use of algorithms that provided highly relevant search results. Central to this success was PageRank, an algorithm that ranked web pages based on their importance and relevance by looking at the number and quality of links pointing to them. The key idea behind PageRank was that if a website was linked to by many others, it was likely more authoritative and thus should rank higher.
As the internet grew, so did Google’s need to evolve its search technology. Over time, Google introduced more complex algorithms such as Hummingbird, RankBrain, and BERT, which leveraged artificial intelligence and machine learning to better understand user intent and deliver more accurate results. Google Search also became more personalized, using information about a user’s location, search history, and other factors to deliver customized results.
In addition to traditional web search, Google introduced specialized searches like Google Images (2001), Google News (2002), and Google Scholar (2004). Over the years, Google has continually improved its search engine with features like instant answers (e.g., weather, sports scores, flight statuses), Knowledge Graph (which surfaces information directly from trusted sources), and featured snippets (direct answers to queries displayed at the top of the results).
Today, Google handles over 3.5 billion searches per day and holds a market share of over 90% globally, making it the dominant search engine by a wide margin.

Online Advertising: Google Ads and AdSense
Google's primary revenue stream comes from online advertising, specifically through its platform Google Ads (formerly AdWords) and AdSense. Google Ads allows businesses to bid for ad placement in Google's search results or across the web via the Google Display Network. The ads can be in various forms, including search ads, display ads (banners), video ads (YouTube), and shopping ads. The system operates on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, meaning advertisers only pay when users click on their ads, making it cost-effective for businesses of all sizes.
The effectiveness of Google Ads lies in its ability to target users based on their search queries and demographic information. Google collects vast amounts of data on users through its various services (e.g., Gmail, YouTube, Android), which allows advertisers to reach highly specific audiences. For example, a user searching for "best smartphones" will see ads for smartphones from various vendors. These ads are auctioned in real-time, and advertisers bid on specific keywords.
AdSense, on the other hand, allows website owners to monetize their content by displaying Google Ads on their websites. Google serves ads that are contextually relevant to the website's content, and the site owner earns a percentage of the ad revenue. AdSense has been particularly popular with bloggers, news sites, and small content creators.
Google’s advertising business is hugely profitable, contributing over 80% of the company’s revenue. In 2022, Google’s total advertising revenue exceeded $220 billion, solidifying its position as the largest online advertising platform in the world.

Android
Android is the world's most popular mobile operating system, developed by Android Inc., which Google acquired in 2005. The decision to purchase Android was strategic, as Google anticipated the shift toward mobile computing. Android’s open-source nature allowed it to be widely adopted by smartphone manufacturers, including major brands like Samsung, LG, Huawei, and Xiaomi. This helped Android achieve a massive market share, powering over 70% of the world’s smartphones.
Android is based on Linux and is highly customizable, allowing manufacturers to create unique user interfaces while still benefiting from Google's ecosystem of services, like Google Search, Gmail, and YouTube. One of the key features of Android is its integration with the Google Play Store, which offers millions of apps for download, making Android devices versatile and feature-rich.
For Google, Android is a vehicle to ensure its services remain central in the mobile world. By embedding apps like Google Maps, Chrome, and Google Assistant into Android devices, Google ensures that users stay within its ecosystem, where they can be served with ads, thus reinforcing Google’s advertising revenue.
Despite its success, Android has not been without controversy. Google has faced multiple antitrust lawsuits in the European Union for allegedly forcing manufacturers to pre-install Google apps, which regulators argued stifled competition. Nevertheless, Android continues to dominate the global smartphone market, particularly in emerging economies.

Gmail
Gmail is Google’s email service, launched in 2004 with a then-revolutionary offering of 1 GB of free storage—far more than competitors like Yahoo and Hotmail were offering at the time. Gmail's user-friendly interface, powerful search functionality, and large storage capacity quickly made it popular among users. Today, Gmail has over 1.5 billion users worldwide, making it one of the most popular email platforms.
A key feature of Gmail is its integration with the broader Google ecosystem, allowing seamless access to services like Google Drive (for cloud storage), Google Calendar, and Google Meet (for video conferencing). Gmail also includes advanced features like spam filtering, category tabs (Primary, Social, Promotions), and conversation view, which organizes emails into threads to make them easier to follow.
Gmail’s monetization strategy is tied to Google's advertising business. Gmail is free to use, but Google serves ads based on user data, such as search queries and email content. Though Google claims that it no longer scans emails for advertising purposes, it still uses AI to analyze email content to provide personalized experiences (e.g., suggesting calendar invites or surfacing important emails).
Gmail is also used by businesses through Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), a subscription-based service that offers custom domain names, more storage, and additional collaboration tools for enterprises.

Google Chrome
Google Chrome is Google's web browser, launched in 2008. It quickly rose to prominence due to its speed, simplicity, and clean interface. Chrome was built on Chromium, an open-source project, and leveraged the V8 JavaScript engine, which made it faster than other browsers at the time, such as Internet Explorer and Mozilla Firefox.
One of Chrome’s defining features is its focus on security and performance. It was one of the first browsers to use a sandboxing technique, which isolates each web page in its process, reducing the risk of malware affecting the system. Chrome also automatically updates to the latest version, ensuring users have the latest security patches.
Chrome’s popularity is tied to its seamless integration with Google’s suite of services, including Google Search, Gmail, and Google Drive. Users can sign into their Google account and sync bookmarks, history, and passwords across devices, creating a cohesive experience across desktops and mobile devices.
By 2020, Chrome had captured over 60% of the global browser market, making it the most widely used browser. Its success also paved the way for Chrome OS, a lightweight operating system used in Chromebooks, which are popular in education due to their affordability and cloud-based functionality.

Google Maps and Google Earth
Google Maps is a web-based mapping service launched in 2005 that offers satellite imagery, street maps, and real-time traffic information. Google Maps has become an essential tool for everyday navigation, offering turn-by-turn directions, local business information, and even real-time updates on public transportation. The service is widely used on mobile devices through the Google Maps app.
One of the defining features of Google Maps is Street View, introduced in 2007. Street View allows users to see panoramic views of streets in cities around the world, offering a virtual experience of places they may want to visit. This feature has been expanded to cover more rural areas, indoor spaces, and even natural wonders, such as the Grand Canyon.

Google Maps has also evolved into a powerful local discovery tool, with users relying on it to find restaurants, hotels, and businesses, complete with reviews and ratings from other users. This integration with Google’s local business directory has made it a valuable platform for businesses seeking visibility.
Google Earth, a related product, allows users to explore the planet through detailed satellite images. It offers a more immersive experience than Maps, with 3D imagery and the ability to "fly" to different parts of the world. Initially launched as a standalone desktop application, Google Earth is now available on the web, offering access to geographic data, interactive storytelling, and educational tools.

YouTube
Google acquired YouTube in 2006 for $1.65 billion. Since then, YouTube has grown to become the largest video-sharing platform in the world, with over 2 billion monthly logged-in users. YouTube is a hub for diverse content, from music videos and movies to educational tutorials and user-generated content like vlogs.
For Google, YouTube represents a crucial part of its advertising ecosystem. YouTube runs ads before or during videos, with advertisers paying for exposure to YouTube’s vast audience. YouTube also introduced YouTube Premium, a subscription service that allows users to watch videos ad-free and access exclusive content.
YouTube's recommendation algorithm plays a key role in keeping users engaged, using machine learning to suggest videos based on users' watch history and preferences. This has led to users spending billions of hours on the platform each day, making it a dominant force in both entertainment and education.
Creators on YouTube can monetize their content through the YouTube Partner Program, earning revenue from ads placed on their videos. Some top creators have turned YouTube into a full-time career, earning substantial income from ads, sponsorships, and merchandise.

Google Cloud
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is Google’s cloud computing service, which provides businesses with infrastructure, data storage, machine learning tools, and analytics capabilities. Launched in 2008, Google Cloud competes with Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, offering services that range from hosting websites to running complex machine learning models.
Google Cloud is built on the same infrastructure that powers Google’s own services, including Google Search and YouTube. This gives it a reputation for speed, reliability, and scalability. GCP provides customers with virtual machines, cloud storage, databases, and developer tools, making it ideal for businesses that want to scale their operations quickly without investing in physical servers.
BigQuery is one of Google Cloud’s standout products, providing a powerful data warehouse solution that allows companies to run fast SQL queries on large datasets. Google Cloud is also known for its advancements in machine learning, offering pre-trained models and services like AutoML, which allows businesses to build custom machine learning models without needing deep expertise in AI.
Despite being smaller than AWS and Azure, Google Cloud is growing rapidly, with a particular focus on data analytics and AI services. In 2022, Google Cloud generated over $26 billion in revenue, becoming an increasingly important part of Google’s overall business.

Hardware Products: Pixel, Nest, and More
While Google is primarily a software and services company, it has ventured into hardware with several successful products. The most prominent is the Pixel line of smartphones, which debuted in 2016. Pixel phones are known for their clean Android experience, receiving updates directly from Google, and for their camera technology, which uses AI to produce stunning images even in low light. The Pixel series has helped Google compete directly with Apple’s iPhone and Samsung Galaxy phones.
In addition to smartphones, Google has developed a range of smart home products under the Google Nest brand, which was initially a separate company that Google acquired in 2014. Google Nest products include smart thermostats, security cameras, and smart speakers. The Google Home line, powered by Google Assistant, competes with Amazon’s Echo line of smart speakers.
Google has also developed Chromebooks, which are lightweight laptops that run on Chrome OS. Chromebooks are particularly popular in education due to their affordability, ease of use, and focus on cloud-based applications. The success of Chromebooks has helped Google gain a foothold in the hardware space, particularly in markets like the U.S. educational sector.
Google’s approach to hardware is deeply integrated with its software ecosystem, ensuring that all its devices work seamlessly with Google services like Google Photos, Drive, and Assistant. This integration is a strategic move to keep users within the Google ecosystem across both hardware and software platforms.

Alphabet Inc.
In 2015, Google underwent a corporate restructuring and created a parent company called Alphabet Inc. Alphabet serves as a holding company for Google and several other companies that Google had acquired or started. The main goal of the restructuring was to separate Google's core internet services (search, ads, YouTube) from its more experimental ventures, such as Waymo (self-driving cars) and Verily (life sciences).
Alphabet allows these different businesses to operate more independently, with their own leadership and funding, without being tied directly to Google’s traditional internet-based business model. For instance, Waymo, Alphabet's autonomous driving subsidiary, is seen as a leader in self-driving technology and is valued in billions, yet it operates separately from Google.
This structure also allows for better transparency for investors, as Alphabet’s quarterly earnings break down the performance of Google and "Other Bets" (which include Waymo, Verily, and other initiatives). It also gives individual business units the freedom to focus on innovation and long-term growth without being overly concerned about Google’s short-term revenue needs.
Alphabet’s structure underscores Google’s ambitions to move beyond being just a search and advertising company and to become a diversified technology conglomerate involved in industries like transportation, healthcare, and urban planning.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Google is at the forefront of AI and machine learning advancements, making significant contributions in this space. Google AI, previously known as Google Research, is responsible for developing AI tools and technologies that are integrated across various Google products.
Key AI and ML Technologies:
- TensorFlow: Google developed TensorFlow, an open-source machine learning framework that enables researchers, developers, and businesses to build and deploy machine learning models. TensorFlow has become a standard tool in the machine learning community, used for applications ranging from natural language processing (NLP) to computer vision.
- DeepMind: Google acquired DeepMind in 2015, a leading AI company famous for its AlphaGo program, which defeated the world champion at Go, an ancient and complex board game. DeepMind has also been involved in advancements in AI for healthcare, protein folding with AlphaFold, and energy-saving initiatives in Google's data centers.
- Google Assistant: Powered by advancements in natural language processing (NLP) and AI, Google Assistant is one of the most advanced virtual assistants available. It allows users to perform a variety of tasks using voice commands, from setting reminders to controlling smart home devices.
- RankBrain and BERT: These AI-driven algorithms significantly improved Google Search by understanding search queries more deeply. RankBrain helps to interpret ambiguous or unfamiliar queries, while BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) allows Google Search to better understand the context of words in searches, improving relevance.

AI in Google Products:
- Google Photos: AI powers features like automatic photo categorization, facial recognition, and memory generation, making photo management easier.
- Google Translate: Neural machine translation (NMT) dramatically improves translation accuracy across hundreds of languages.
- Google Lens: An AI-powered visual search tool that allows users to identify objects, translate text, and interact with the physical world through their smartphone camera.
In addition to consumer-facing products, Google uses AI internally for improving advertising algorithms, optimizing energy consumption in data centers, and advancing its autonomous driving project under Waymo.

Waymo: Google’s Autonomous Driving Project
Waymo, originally part of Google X (the company’s moonshot project division), is one of the most well-known autonomous vehicle companies globally. Waymo is developing self-driving cars with the goal of improving transportation safety, reducing traffic accidents, and offering a new form of mobility.
- Autonomous Technology: Waymo uses a combination of LiDAR, radar, cameras, and machine learning algorithms to detect and interpret the environment in real-time, making driving decisions such as stopping at traffic signals, changing lanes, and avoiding obstacles.
- Testing and Deployment: Waymo has conducted millions of miles of testing both in simulated environments and real-world settings. Phoenix, Arizona, was one of the first areas to have a fully autonomous ride-hailing service, Waymo One, which allows users to book rides in self-driving cars.
- Partnerships: Waymo has partnered with automakers like Chrysler and Jaguar to integrate its autonomous driving technology into their vehicles.

Quantum Computing: Google’s Quantum AI
Quantum computing is another area where Google is pushing boundaries. Google has a specialized division called Quantum AI that focuses on the development of quantum computers, which are expected to revolutionize computation by solving problems that are intractable for classical computers.
Key Milestones:
- Quantum Supremacy: In 2019, Google claimed to have achieved quantum supremacy with their quantum processor Sycamore. This means that their quantum computer could perform a calculation in 200 seconds that would take the world's fastest classical supercomputer 10,000 years to complete.
- Quantum Processors: Google is developing quantum processors with the aim of solving complex problems in materials science, drug discovery, and encryption.
- Partnerships and Research: Google collaborates with academic institutions and research organizations worldwide to advance the field of quantum computing, as it is still in its early stages but holds vast potential for future applications.


Google X (X Development)
Google X, now known as X Development, is Google’s secretive research and development division focused on creating breakthrough technologies, often referred to as "moonshot" projects. The goal of X is to solve major global problems using advanced technology.
Major Projects:
- Project Loon: An ambitious project to provide internet access to remote and underserved areas using high-altitude balloons that act as mobile cell towers. Although Project Loon was eventually discontinued in 2021, it demonstrated Google’s commitment to addressing global connectivity challenges.
- Wing: A drone delivery service designed to transport goods more efficiently, especially in rural or hard-to-reach areas. Wing has already begun trials in the U.S., Australia, and other countries, delivering items like food, medical supplies, and consumer goods.
- Google Glass: Google X developed Google Glass, an augmented reality headset that initially launched in 2013. While the consumer version didn’t gain wide adoption, the technology found its niche in enterprise applications, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics, where workers can benefit from hands-free, heads-up access to data.
Ethical Challenges and Controversies
Despite its numerous successes, Google has also faced ethical challenges and controversies throughout its history.
Key Issues:
- Data Privacy: Google has been criticized for its extensive data collection practices, especially regarding user data from Gmail, YouTube, and Android devices. Concerns have been raised about how this data is used to fuel its advertising business, and in response, Google has enhanced transparency by introducing privacy tools and more robust controls for users.
- Antitrust Cases: Google has faced multiple antitrust investigations worldwide, especially in the U.S. and European Union. The EU has fined Google several times for anti-competitive practices, including bundling its apps with Android and manipulating search results to favor its own services, such as Google Shopping.
- Project Maven: Google’s involvement in Project Maven, a U.S. military AI project, caused internal protests from employees who believed the company’s AI technologies should not be used for warfare. This led to Google not renewing the contract with the Pentagon and creating a new set of AI ethical guidelines.
- Workplace Issues: Google has been accused of mishandling sexual harassment cases internally, which resulted in a massive employee walkout in 2018, demanding better protections for workers and more transparent policies regarding harassment and discrimination.
Ethical AI and Governance:
In response to growing concerns, Google has established the AI Principles, a set of ethical guidelines that govern the development and deployment of its AI technologies. These principles emphasize fairness, accountability, and the avoidance of bias, especially in sensitive areas like healthcare, facial recognition, and law enforcement.

Sustainability Initiatives
Google has made significant commitments to environmental sustainability. The company has been carbon neutral since 2007, and in 2020, Google announced its goal to run all its data centers and offices on carbon-free energy 24/7 by 2030.
- Renewable Energy: Google is one of the largest corporate purchasers of renewable energy in the world, using solar, wind, and other clean energy sources to power its massive data centers. The company has also invested in renewable energy projects globally.
- Google Earth and Environmental Projects: Google uses Google Earth to monitor deforestation, track wildlife populations, and provide critical data for researchers studying climate change. Google also supports Project Sunroof, a tool that helps homeowners estimate the potential solar energy savings for their homes based on Google Earth imagery.
- AI for Climate Change: Google’s AI initiatives are being used to track emissions, predict deforestation, and optimize energy usage. Google Cloud is also collaborating with environmental organizations to provide better data and tools for climate change mitigation.